Introduction
In the food industry, safety is of utmost importance, and ensuring that products are free from contamination is an ongoing challenge. To tackle these risks, food safety management systems such as HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) play a vital role. Understanding the concept of a critical control point (CCP) within this system is essential for preventing food contamination and maintaining high-quality products.
This blog will explore what a critical control point is in HACCP, its significance, and how it contributes to food safety, with particular attention to key technologies like machine x-ray and automated production systems.
What Is HACCP and Why Is Food Safety Important?
HACCP, which stands for Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point, is a preventive food safety management system used in the food industry. Its purpose is to identify, evaluate, and control food safety hazards. The main goal of HACCP is to prevent foodborne illnesses by closely monitoring critical steps in food production.

Why Is Food Safety Important?
Food safety is crucial for protecting consumers from health risks associated with contaminated food. Food contamination can result in product recalls, outbreaks of illness, and, in severe cases, fatalities. The repercussions of these incidents can be significant and include legal actions, financial losses, and harm to a company’s reputation. By implementing Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), food producers can systematically minimize the risk of contamination, thereby enhancing food quality and safety.
The primary hazards in food safety include:
Physical Contamination: This involves foreign objects such as glass, metal, or plastic that may end up in food products.
Chemical Contamination: This includes harmful substances like pesticides, allergens, and other chemicals.
Biological Contamination: This refers to pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can contaminate food.
The Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) system helps businesses identify these risks and implement controls at critical points to prevent or reduce these hazards.
What Is a Critical Control Point in HACCP?
A critical control point (CCP) in the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system is a specific step in the food production process where control measures can be implemented to prevent, eliminate, or reduce a food safety hazard to an acceptable level. Not all steps in food production are considered CCPs; only those where a hazard is likely to occur and can be effectively controlled qualify as CCPs.
Key Characteristics of Critical Control Points (CCPs)
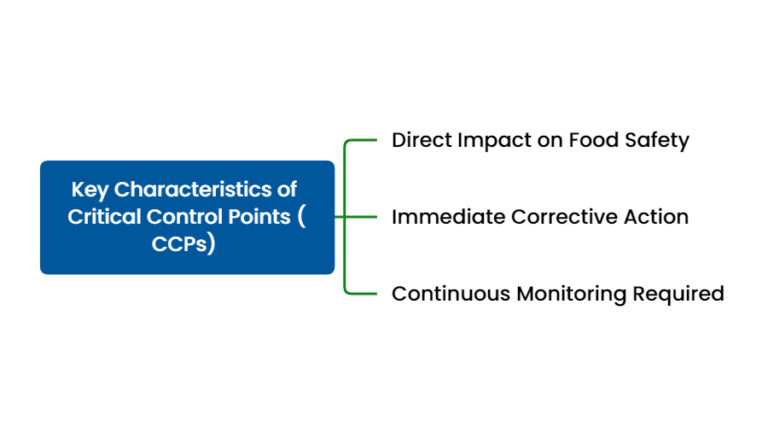
Direct Impact on Food Safety: Control at this point is crucial for ensuring that food is safe for consumption.
Continuous Monitoring Required: A critical control point must be monitored continuously to ensure that the process stays within established limits.
Immediate Corrective Action: If a critical limit is exceeded, immediate corrective actions must be taken to regain control.
Examples of Critical Control Points in Food Production
- Cooking temperatures for meat
- The use of metal detectors to prevent physical contamination
- X-ray inspection machines to identify foreign objects
- Cooling processes for perishable foods
CCPs are identified during the hazard analysis phase, which involves mapping the entire production process to pinpoint potential hazards and determine which stages require control.
Identifying and Monitoring Critical Control Points in HACCP
Identifying Critical Control Points (CCPs) is a crucial element of the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) food safety system. This process entails a thorough evaluation of the production process to pinpoint areas where the risk of contamination is highest and where effective control measures can be implemented.
Steps to Identify CCPs
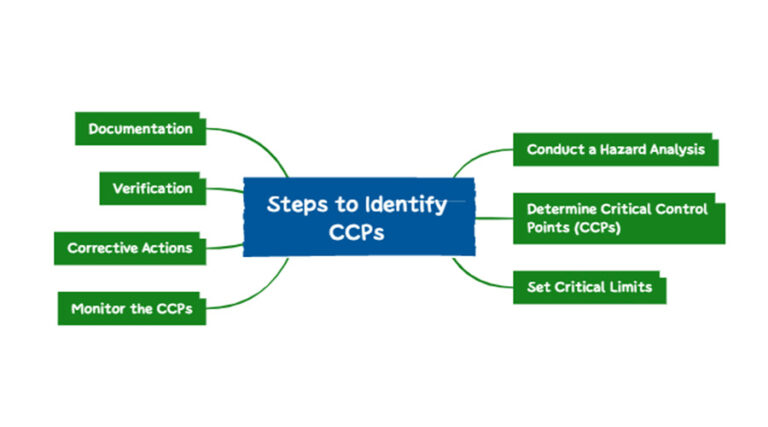
1. Conduct a Hazard Analysis: Analyze the food production process to identify potential contamination points.
2.Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs): Based on your analysis, identify the steps in the process that are CCPs, where control is necessary to prevent or reduce contamination.
3. Set Critical Limits: Establish specific maximum or minimum limits for each CCP, such as temperature, time, or pH level.
4. Monitor the CCPs: Implement monitoring systems to meet critical limits. For instance, you might use automated production systems to track temperature during cooking or cooling.
5. Corrective Actions: If a CCP exceeds or falls below its critical limit, take corrective actions immediately to maintain food safety.
6. Verification: Regularly verify that the CCPs are functioning as intended through inspections and testing.
7. Documentation: Maintain accurate records for auditing purposes and traceability.
How Can You Prevent Physical Hazards?
Modern food processing plants utilize various technologies and automated systems to prevent physical contamination. Machine X-ray systems and metal detectors are commonly employed to detect foreign objects such as metal, plastic, or glass in food products. These technologies ensure that any contaminants are identified and removed from the production line before the products reach consumers.
Role of Automated Systems in Monitoring Critical Control Points
In modern food production, automated product systems are indispensable for ensuring the continuous monitoring and control of CCPs. These systems can monitor temperature, time, and other critical factors, and they can also integrate with other technologies, such as machine X-rays and metal detectors, to enhance food safety.
How Automated Systems Contribute to Food Safety
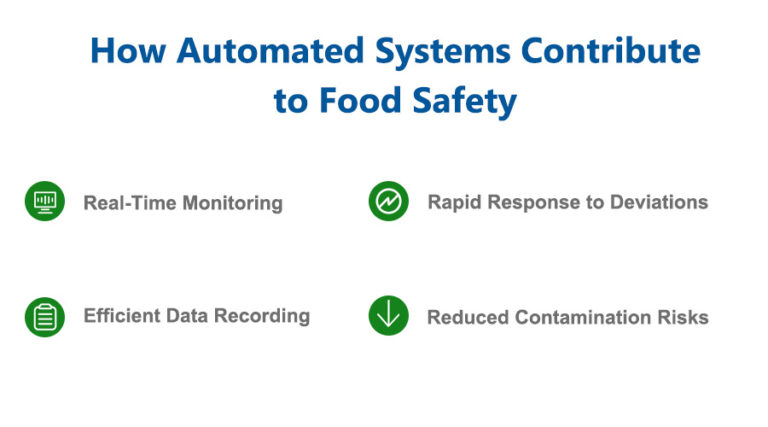
1. Real-Time Monitoring: Automated systems continuously monitor critical control points (CCPs) 24/7, eliminating the risk of human error.
2. Efficient Data Recording: These systems automatically document data, ensuring that all critical control points are accurately recorded for regulatory compliance and auditing purposes.
3. Rapid Response to Deviations: When deviations from critical limits occur, automated systems can trigger alarms and initiate corrective actions immediately.
4. Reduced Contamination Risks: Technologies such as X-ray inspection machines are effective in detecting even the smallest contaminants, significantly lowering the risk of physical contamination.
Machine X-ray systems, particularly bone X-ray systems, are especially useful for identifying foreign materials or small bones in sealed packaging or bulk food products. These systems scan food items to detect contaminants like metal fragments, glass, or plastic.
Impact on Food Industry Recalls
By monitoring Critical Control Points (CCPs) more effectively, these systems greatly reduce the chances of contamination reaching consumers. This proactive approach not only minimizes the risks of costly food recalls but also protects a company’s reputation. Early detection of contaminants allows for the rejection of problematic batches before they enter the supply chain, thereby safeguarding both consumers and brands.
Benefits of Implementing Critical Control Points in Food Safety
Implementing critical control points in the food safety process provides multiple advantages for food producers. These benefits go beyond merely adhering to food safety regulations; they also include improvements in product quality, operational efficiency, and enhanced consumer trust.

Benefits of Critical Control Points (CCPs)
1. Improved Food Safety: CCPs directly address potential hazards, significantly reducing the risk of contamination and foodborne illnesses.
2. Higher Food Quality: Food producers can ensure the consistency and quality of their products by maintaining control over the production process.
3. Operational Efficiency: Automated systems for monitoring CCPs decrease the need for manual inspections, streamlining production processes and saving both time and resources.
4. Consumer Trust: Companies that uphold high food safety standards are more likely to gain consumer trust, which fosters brand loyalty.
5. Regulatory Compliance: Following Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) guidelines and maintaining accurate records of CCPs helps businesses comply with food safety regulations and avoid legal penalties.
By effectively implementing CCPs, food producers can protect public health, minimize the risk of product recalls, and enhance operational efficiency, all while ensuring consumers receive safe, high-quality food.
Conclusion
Understanding critical control points (CCPs) within the Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) system is vital for ensuring food safety, preventing contamination, and maintaining high-quality standards in food production. By identifying CCPs and utilizing automated systems such as x-ray inspection machines and metal detectors, food producers can effectively mitigate risks and decrease the chances of food contamination. This proactive approach helps to foster consumer trust. The importance of CCPs in the HACCP food safety system is paramount; they play a crucial role in protecting public health and maintaining brand integrity.
FAQs
HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) is a food safety management system that identifies and controls food safety hazards at critical points in the production process to prevent contamination and ensure product safety.
A critical control point (CCP) in HACCP is a specific stage in the food production process where measures can be implemented to prevent, eliminate, or significantly reduce a food safety hazard to an acceptable level.
Food contamination can arise from biological, chemical, or physical hazards. The leading causes include improper handling, inadequate sanitation, cross-contamination, and failure to maintain critical control points during production.