Food safety is a primary concern in every part of the world. Countries worldwide lose significant amounts of their gains because of the effects of food safety hazards. Low- and middle-income countries spend at least 95.2 billion U.S. Dollars yearly on foodborne diseases. These foodborne diseases typically occur due to three major types of food safety hazards.
These hazards make foods unsafe for consumption, and they cause different body reactions when eaten. Therefore, it is crucial to understand how to properly identify and address these hazards promptly. Here, you will get more familiar with the three food safety hazard categories, their causes, and how to prevent them effectively.
Biological Hazards
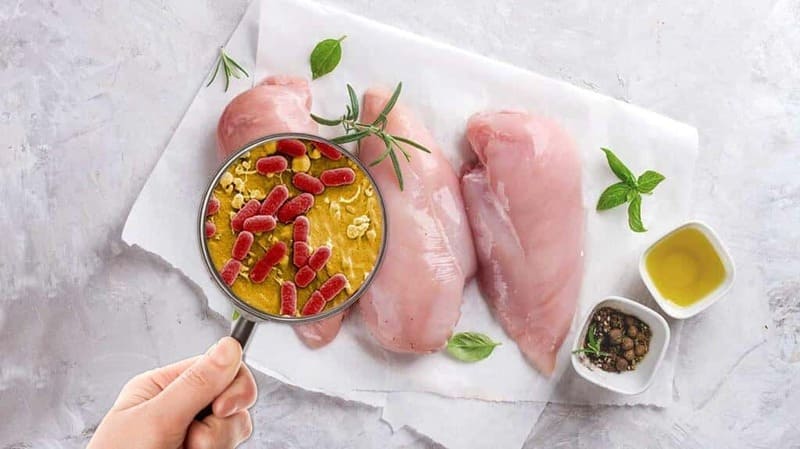

Biological hazards occur when foods get contaminated by living organisms like fungi, yeast, parasites, bacteria, and viruses. They are arguably the most common hazards of food consumption. This is because microorganisms exist everywhere, including in water, air, humans, and animals.
These microorganisms may either be naturally present in foods or may be introduced through contamination. They can cause serious foodborne diseases if they find their way to our food. These illnesses usually vary from gentle or mild to severe or critical conditions.
Generally, foods like vegetables, fruits, poultry, meat, dairy products, and moist foods are prone to contamination. For example, unpasteurized milk and ground beef are often candidates for E. coli attacks. Other common biological hazards include:
- Norovirus
- Salmonella
- Clostridium perfringens
- Listeria
- Campylobacter
Which Factors Can Cause Biological Hazard?
Biological food hazards, especially bacteria and viruses, transfer quickly to food through cross-contamination. Cross-contamination occurs when naturally occurring organisms on food handlers are transmitted to foods.
These are some of the significant causes of biological hazards:
- Raw Materials. All food substances have their respective microorganisms present in them. Raw materials like vegetables, root crops, and fruits are especially receptive to soil-borne pathogens. Thus, these food items often require thorough cleaning and pretreatment before consuming.
Water. Most foods we cook often get in contact with water, and water gets contaminated in cases when the source is infected. Water is a common carrier of pathogens such as Norovirus, Hepatitis E, Escherichia coli, and other pathogens. Since water is a significant ingredient in nearly all operations in the food industry, it is capable of transferring these contaminating agents.
- Food Packaging Materials. Packaging materials like cartons, plastics, and cans are usually prone to biological hazards. Food packaging materials often get in direct contact with food substances. Therefore, it is crucial to put packaging materials through adequate sterilization processes.
- Pests. Pests such as rodents, insects, lizards, and birds are good examples of pathogen carriers. These pests have easy access to restaurants and other food stores. Their hair, feces, urine, and other waste products can easily fall into the stored food, thereby contaminating it.
Prevention Methods
Despite their natural occurrence, it is possible to control biological contaminations. Below are some hygiene and food safety practices to prevent them from multiplying:
Use Professional Detecting Equipment
The load of pathogens present in food materials can determine how contaminated they are. Therefore, there is a need to employ professional and efficient equipment to detect the presence of these organisms. The equipment you can use include an X-ray inspector system, metal detector, etc.
Examples of metal detectors you can use include the following:
Conveyor Metal Detector. You can detect metal contaminants during food processing using this equipment. It has high stability and sensitivity for detecting various kinds of metals. You can use it for every kind of packaging product, including bread, meat, sausages, etc.

Likewise, you can use X-ray inspection systems like:
X-Ray Inspection System for Packaged Products. This tool helps to detect contaminants like glass, bones, sand, stones, glass, metals, desiccants, and more. It is suitable for all kinds of packaged food products.
Clean Food Processing Equipment Frequently
Your cleaning routines for food contact materials, kitchen equipment, cabinets, counters, etc., must be thorough and timely. Ensure the use of effective concentrations of soap and other cleaning products that will not cause hazards in the food.
Practice Adequate Food Hygiene
Since biological contaminants are usually transmitted by cross-contamination from food handlers to the food material. Therefore, you can prevent the transfer of contaminants through proper hand washing, wearing protective gear, and using clean clothes.
Physical Hazards
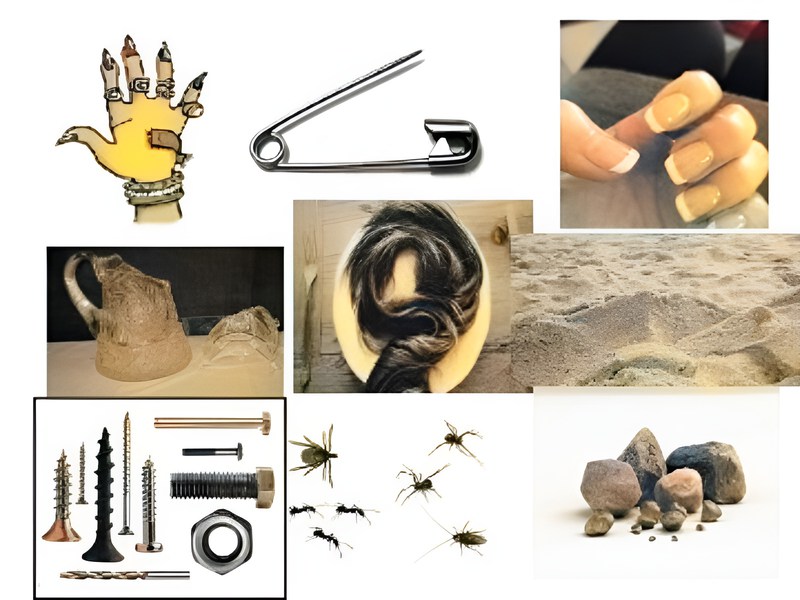

Physical hazards happen when foreign objects find their way into food materials. Such objects include stones, glass, shells, bones, metal fragments, etc. These foreign bodies can easily cause bruises, cuts, and choking.
However, there are other physical hazards that act as growth agents for pathogens. They include human or animal hair, soil or sand, pest droppings, inedible leaves, and many more.
Physical hazards may be naturally present in foods like fruit stems, seafood shells, or bones from meat. Food handlers also play a part in the unnatural contamination of food materials when nails and hair strands fall into food during processing.
Which Factors Can Cause Physical Hazards?
Some of the factors causing physical hazards include:
- Raw Materials. There are situations when physical hazards result from the raw materials themselves. For instance, bones from meats are sometimes impossible to remove altogether, and these bones can cause the consumer to choke. Likewise, twigs and leaves found on fruits are easy carriers of pathogens. Food materials such as sugar, flour, and salt will likely be contaminated with small rocks.
- Food Handlers. Physical hazards can also occur due to the food handler’s lack of proper hygiene. This is why gears such as hair caps and nets, gloves, and nose covers are mandatory for food handlers. These protective wearings help prevent false nails, hair strands, and other objects from finding their way into the food when preparing it.
Pests. Pests have different ways of contaminating food materials. Rodents can drop strands of hair carrying tons of pathogens. Likewise, insects can die and break into pieces as they mix with food, while birds can make droppings anywhere in the storage unit where they can easily get into stored foods.
- Production Equipment. Old and rusty equipment can cause chips of plastics and metals to fall into food materials and mix with them during processing. Physical hazards like screws, broken glasses, nails, and other foreign substances can mix with food in the kitchen or production unit.
Prevention Methods
Although physical contaminants are larger, there are a few ones that can be hard to detect. Here are some things to put in place to prevent physical food safety hazards:
Use Advanced Inspection Systems
You can employ machines like metal detectors, magnets, and AI-powered detection systems. These systems can efficiently and significantly help remove physical contaminants from food materials.
Some highly advanced inspection systems you can use include:
- Compact X-Ray Inspection System for Small Products. This automated system is most effective for small items like seasoning cubes, biscuits, etc. It can detect metals, ceramics, glass, stones, bones, etc.
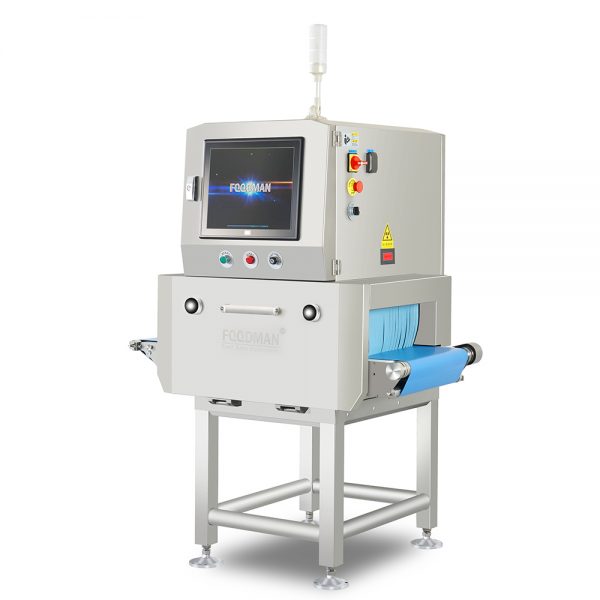

- Single beam X-Ray Inspection Systems for Canned Products. It is specially designed to ensure safe food processing, with the ability to detect contaminants in canned products.
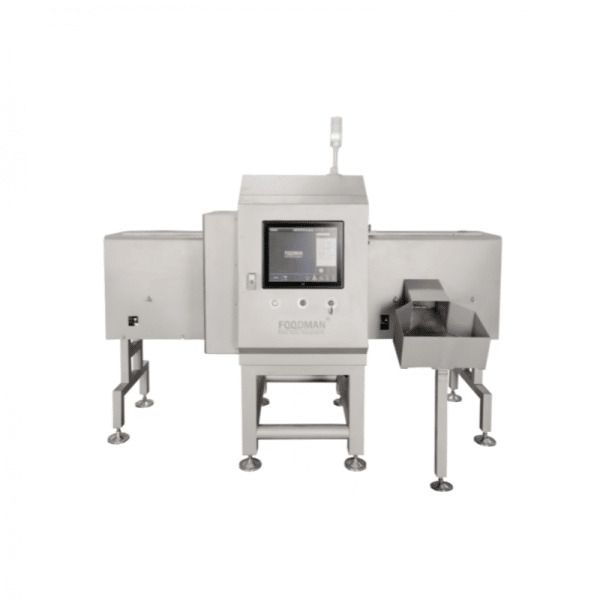

Ensure Good Manufacturing Practices
There are basic food hygiene and safety tasks that can help you prevent possible hazards. These practices include wearing the right attire during food processing, avoiding jewelry, neatly trimming nails, and using hairnets in the kitchen area.
Inspect Potential Sources of Physical Hazards and Remove Them
Food handlers should check out for both field and storage area contaminations. These include stones, soil, hair, dropping, pests, and many more. Identify these materials and remove them appropriately.
Chemical Hazards
The presence of chemical substances in food meant for consumption causes chemical hazards in foods. These chemicals contaminate the food, therefore, making it unsafe for consumption. Most of the chemicals exist naturally or are put in foods for processing purposes.
Naturally occurring chemicals such as saponins in legumes are present as toxin defense of plants. They help prevent the plants from insects and microorganisms. A high dosage of this compound can be risky and harmful. As a result of this, pretreatment of legumes is compulsory. Other naturally occurring chemicals in foods are lectins, tetrodotoxin, and mycotoxins.
In most cases, food additives and preservatives can act as chemical contaminants. They become hazardous when applied in high amounts or with inappropriate labeling. Meanwhile, there are unintentional chemical hazards such as fertilizers, machine oil, pesticide residues, antibiotics, and heavy metal compounds.
Which Factors Cause the Chemical Hazards?
- Heat Treatment. Chemical hazards occur majorly as a result of improper processing. With acryl amide, inspectors can indicate that a food has been processed with extremely high heat.
- Additives and Preservatives. The unregulated usage of additives and preservatives can result in their contamination. Some of these substances can cause negative allergic reactions.
- Soil Amendments. The quality of soil and the amendments applied to it affects the outcome of products while growing raw materials like fruits and vegetables. Plants take in unwanted chemicals from the ground and fertilizers that were used to grow them.
- Cleaning Agents. Sanitizing solutions or substances like chlorine harm food quality and safety. Unintentional chemical hazards can occur when these substances get into foods.
Prevention Methods
You can prevent chemical food safety hazards by following the following tips:
Ensure Proper Labeling and Storage of Chemicals
Every chemical used in food processing must be properly labeled. The label must contain the name of the chemical, the usage procedure, and the appropriate amount to use. This will ensure that there will be no problem of misuse or overuse. Also, these chemicals should have dedicated storage locations not close to the food preparation area.
Adequate Training and Strict Compliance
Food handlers need proper orientation and training on using chemicals for cleaning and cooking foods. They must also know how to handle these chemicals properly by using protective gear. No residues must remain after cleaning or sanitation.
Commit to Food Safety Standards
There are established standards for the adequate amounts of chemicals for food processing. You should always refer to these references to avoid overuse or misuse of chemicals that may cause adverse health effects.
Conclusion
Food safety hazards threaten the health of consumers, causing several foodborne illnesses. Complications can result from the natural causes of food hazards, the surrounding environment, and even some misconduct by food handlers.
However, food safety hazards can be prevented or well-managed with proper identification, processing, and monitoring procedures. The use of advanced inspection machines, metal detecting equipment, safe cleaning solutions, and other precautionary steps help to reduce food hazards to a minimum.